Electric Current
Electric current is the ordered (directed) movement of charged particles.
Current Source
A current source is a device for creating and maintaining an electric field. In current sources, charges are separated at the poles; as a result of this separation,
all types of energy are converted into electrical energy.
Types of Current Sources:
-
Electric machine
-
Thermoelement
-
Chemical elements (batteries, accumulators, etc.)
-
Photoelement
-
Solar battery
Electric Current in Metals
Electric current in metals is the ordered movement of free electrons. The direction of electric current is conventionally taken as the direction in which positively
charged particles would move, i.e., from "+" to "-", but through the entire circuit.
Effects of Electric Current
- Chemical Effect of Electric Current — obtaining pure metals from their solutions. Application: in galvanic baths, products are coated (sprayed) with
valuable metals.
- Thermal Effect of Current — heat release from a heating element (electric furnace, iron). Application: for cooking, lighting, heating a room.
- Magnetic Effect of Current — the phenomenon of interaction between a body with current and a magnet. Application: the magnetic effect of a coil with
current and a magnet is used in the device called a galvanometer.
Current Strength
Current strength is a physical quantity that characterizes the amount of electricity passing through the cross-section of a conductor per unit of time.
-
I — current strength
-
q — amount of electricity
-
t — time
Formula for determining current strength:
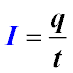
Units of measurement for current strength:
-
1 Ampere (A)
-
1 KiloAmpere (KA) = 1000 A
-
1 milliAmpere (mA) = 0.001 A
Voltage
Voltage is a physical quantity that characterizes the electric field created by electric current in a section of the circuit.
-
U — voltage
-
A — work
-
q — charge
Formula for voltage:

Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity characterizes the ability of a conductor to conduct electric current.
-
k — proportionality coefficient (S, Siemens)
-
I — current strength
-
U — voltage
Formula for electrical conductivity:

Unit of measurement for electrical conductivity:
-
1 S (Siemens) — electrical conductivity of a conductor through which a current of 1 A flows, and the voltage at the ends of the section is 1 V.
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law for a section of a circuit: the current strength in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance of the circuit.

-
R — resistance (Ohm)
-
I — current strength
-
U — voltage
Resistance
Resistance is a physical quantity that characterizes the ability of a conductor to conduct electric current. Resistance depends on the parameters of the conductor and the substance.
-
l — length of the conductor (m)
-
S — cross-sectional area (mm²)
-
σ — specific resistance of the conductor (Ohm)
Formula for finding the resistance of a conductor:

Electrical Power
Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The unit of power is the watt (W).
Formula for electrical power:
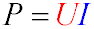
-
P — power (W)
-
U — voltage (V)
-
I — current strength (A)
Energy Consumption
Energy consumption in electrical devices is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It represents the amount of energy used over time.
Formula for energy consumption:
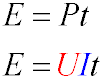
-
E — energy (kWh)
-
P — power (kW)
-
t — time (h)
Components of an Electric Circuit
- Resistor — a conductor with a certain resistance. It is used to change the resistance in the circuit.
- Rheostat — a device used to regulate the current strength in the circuit.
- Potentiometer — a device used to regulate and distribute the current strength in the circuit.
Electricity and Magnetism |
Описание курса
|

