|
Economics Tasks on the Topics: Calculating Labor Productivity and Labor Intensity
Note: The problems is taken from the forum without changes.
In this lesson:
- Increase in labor productivity based on percentage indicators
- Change in percentage labor productivity
- Increase in labor productivity based on change in labor intensity
- Change in productivity with change in production volume
- Change in productivity with decrease in labor intensity and number of personnel
- Change in the number and volume of production
- Determine labor productivity for commercial products
- Change in labor productivity as a result of change in the number and output
- Change in labor productivity as a result of change in fulfillment of production standards
- Change in labor productivity with decrease in labor intensity of the product
- Change in labor intensity with change in labor productivity
- Calculations with change in productivity growth and labor intensity simultaneously
- Determine the decrease in labor intensity due to increase in labor productivity
- Increase in labor productivity due to several measures
Problem 1. Increase in Labor Productivity Based on Percentage Indicators
Given:
- Total number of workers at the enterprise: 3650
- Number of workers whose productivity increased: 100
- Increase in productivity for these 100 workers: 2.5%
Solution:
-
Calculate the number of workers whose productivity did not change: [ 3650 - 100 = 3550 ]
-
Determine the new productivity level for the entire workforce:
( 3550 * 100% + 100 *102,5% ) / 3650 = 100,07% (More precisely, 100.0684932%)
-
Calculate the increase in labor productivity: 100,07% - 100% = 0,07%
Answer: The increase in labor productivity was 0.07%.
Problem 2. Change in Percentage Labor Productivity
Given:
- Group 1 of activities: +2%
- Group 2 of activities: -4%
- Group 3 of activities: -12.5%
Solution:
-
Calculate the indices of labor productivity for each group of activities:
IGroup 1 = (100 + 2) / 100 = 1.02 ;
IGroup 2 = ( 100 - 4 ) / 100 = 0.96 ;
IGroup 3 = ( 100 - 12.5 ) / 100 = 0.875 ;
-
Determine the overall change in labor productivity: To find the overall change, multiply the indices:
Itotal = 1.02 x 0.96 x 0.875 ≈ 0.8574
-
Convert the index back to a percentage change: ( Itotal - 1) x 100% = (0.8574 - 1) x 100% ≈ -14.26%
Answer: The overall change in labor productivity is approximately -14.26%.
Problem 3. Increase in labor productivity based on changes in labor intensity
Calculate the increase in labor productivity in conventional physical terms at a soap factory
if the data on soap production and the number of man-days worked are known.
Coefficients for converting into conventional soap: laundry soap - 1.0, toilet soap - 1.8, soap shavings - 2.2.
|
Name of the indicator
|
Base period
|
Report Period
|
|
Man-days worked
|
160
|
170
|
|
Laundry soap produced, t
|
100
|
200
|
Toilet soap produced, t
|
75
|
65
|
|
Soap chips produced, t
|
90
|
95
|
Comment.
The essence of this task is to evaluate labor productivity in the conditions of a changing range of production and working time fund.
First, we must reduce the entire production program to a certain conventional product. After that, find out what quantity of these
same conventional products were produced per unit of time, which will express labor productivity in conventional-natural measurement.
The ratio of these figures will give us an increase in labor productivity.
Solution.
Let's reduce the production program to a single measure - conventional products.
The production program in conventional products for the base period is:
100 + 1.8 * 75 + 90 * 2.2 = 433
The production program in conventional products in the reporting period is:
200 + 1.8 * 65 + 2.2 * 95 = 526
Since the working time fund was different, we will determine the output for one man-day
in the base period:
433 / 160 = 2.70625
in the reporting period:
526 / 170 = 3.09412
The growth in labor productivity of the reporting period to the base period, respectively, will be equal to:
3.09412 / 2.70625 = 1.14332 or 14.3%
Answer: the growth in labor productivity was 14.3%
Problem 4: Change in Productivity with Change in Production Volume
Determine how labor productivity will change if the change in production volume is +11%
and the change in the number of employees is +5.
Solution:
To find the change in labor productivity, calculate the indices of production volume and number of employees
and substitute the obtained values into the formula:
Ipt = Iv / Ih
Where:
- Ipt is the labor productivity index.
- Iv is the production volume index.
- Ih is the employee number index.
Let’s solve the problem:
Iv = (100 + 11 ) / 100 = 1.11
Ih = ( 100 + 5 ) / 100 = 1.05
Ipt = 1.11 / 1.05 = 1.057
Answer: Labor productivity increased by 5.7%.
Problem 5: Change in Productivity with a Decrease in Labor Intensity and Number of Personnel
Determine how labor productivity will change in the planning year if it is assumed that the number of main workers will decrease
from 450 to 430 people. At the same time, a number of measures are planned that will reduce labor intensity by 9%,
and it is also possible to increase productivity due to organizational measures by 7%.
Solution:
- Find the index of the number of workers:
Ih = 430 / 450 = 0.955
The number of personnel decreased by 4.5%.
- Find the change in labor productivity due to a decrease in labor intensity:
Labor productivity - the reciprocal of labor intensity
Δpt = 100% - 100% / (100% - 9% ) ≈ 9.89%
Labor productivity increased by 9.89% due to a decrease in labor intensity.
- Find the production volume index:
Iv = ( 100% + 7% ) / 100% = 1.07
- Find the labor productivity index due to a decrease in labor intensity:
Ipti = ( 100% + 9.89% ) / 100% = 1.0989
- Find the final productivity index using the formula:
Ipt = 1.07 / 0.955 * 1.0989 ≈ 1.22976
Answer: Labor productivity increased by 22.976%.
Problem 6: Change in the Number and Volume of Production
In the base year, the number of workers was 330. In the planning year, it is planned to increase the number of workers by 10%.
The volume of manufactured commercial products is 4 550 000 USD, and in the planned year, the increase in production volume
is expected to be 6%. Determine labor productivity in the base and planned years, and determine the change in labor productivity
in absolute and relative terms.
Solution:
- Find labor productivity in the base year using the formula:
Pt = V / Ch
Where:
- (V) is the volume of production.
- (Ch) is the number of workers.
- (Pt) is labor productivity.
Pt = 4 550 000 / 330 ≈ 13 788 USD/person
- Find the change in the number of workers and the volume of production in the planned year:
Chpl = 330 * 1.1 = 363 workers
Vpl = 4 550 000 * 1.06 = 4 823 000 USD
- Find labor productivity in the planned year:
Ptpl = 4 823 000 / 363 ≈ 13 286 USD/person
- Find the change in labor productivity in relative terms:
IPt = 13 286 / 13 788 ≈ 0.964
Labor productivity decreased by 3.6%.
- Find the decrease in labor productivity in absolute terms:
ΔPt = 13 788 - 13 286 = 502 USD
Answer:
- Ptb = 13 788 USD / person
- Ptpl = 13 286 USD / person
- IPt= 0.964
- ΔPt = - 502 USD
Problem 7: Determine Labor Productivity for Commercial Output
Determine the labor productivity of workers employed at the enterprise if it is known that the volume
of commercial output is 2 950 thousand USD, and the number of workers is 58 people.
Solution:
Labor productivity is an indicator of the efficiency of personnel. It is the amount of products produced by a worker per unit of time.
Pt = V / Ch
Where:
- (V) is the volume of marketable products.
- (Ch) is the number of employees.
Let’s find labor productivity:
Pt = 2,950,000 / 58 ≈ 50 862 USD / person
Answer: Labor productivity was 50 862 USD of marketable products per person.
Problem 8: Change in Labor Productivity as a Result of Changes in the Number and Output
In the planning year, the output of product B increased by 30%. The number of workers increased by 2 people.
In the base year, the number of workers was 274 people. The number of other categories of workers does not change.
Determine how the labor productivity of the main workers engaged in the production of product B will change.
Solution:
The change in labor productivity of workers is calculated using the formula:
ΔPT = Iv / Ih
Where:
- Iv is the index of commercial output.
- Ih is the index of workers.
The numerator takes into account the change in the volume of production, and the denominator takes into account
the change in the number of workers. These values are used as indices.
- Find the change in the number of employees at the enterprise:
Ih = ( 274 + 2 ) / 274 = 1.0073
- Find the index of commercial output:
Iv = 1.30
- Find the change in labor productivity:
ΔPT = 1.30 / 1.0073 ≈ 1.291
Labor productivity increased by 29.1%.
Answer: Labor productivity increased by 29.1%.
Problem 9: Change in Labor Productivity as a Result of Change in Fulfillment of Production Standards
In the base period, workers on average fulfilled time standards by 115%. After the introduction of organizational and technical measures,
time standards began to be fulfilled by 125%. How did labor productivity change as a result?
Solution:
Along with the labor productivity indicator, there are indicators of fulfillment of time standards and fulfillment of production standards.
- Fulfillment of time standards is the time required to produce one product.
- Production standard is the amount of product that must be produced per unit of time.
The percentage of fulfillment of standards is determined as the ratio of actual indicators to planned indicators.
- Calculate the change in labor productivity:
ΔPT = ( 125 / 115 ) * 100% - 100% ≈ 8.7\%
Answer: Labor productivity increased by 8.7%.
Problem 10: Change in Labor Productivity with a Decrease in the Labor Intensity of the Product
The labor intensity of the product decreased by 15%. Determine how labor productivity will change.
Solution:
The labor intensity indicator is the inverse of the labor productivity indicator. There are inversely proportional relationships between labor productivity and the labor intensity of a product.
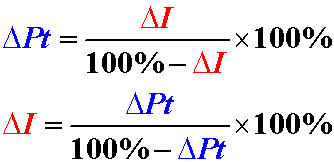
- ΔI is the percentage decrease in labor intensity of a product.
- ΔPt is the percentage increase in labor productivity of a product.
- Find the change in labor productivity:
ΔPT = 15% / ( 100% - 15% ) * 100 ≈ 17.65%
Answer: Due to a 15% decrease in labor intensity, labor productivity increased by 17.65%.
Problem 11: Change in Labor Intensity When Labor Productivity Changes
Determine how the labor intensity of a manufactured product will change if it is known that the change in labor productivity is 20%.
Solution:
Let’s calculate the change in labor intensity using the formula:
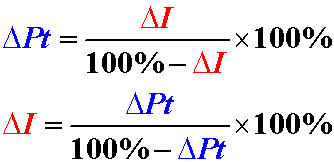
- ΔI is the percentage change in labor intensity.
- ΔPt is the percentage change in labor productivity.
Calculate the change in labor intensity:
ΔI = 20% / (100% - 20%) * 100% = 25%
Answer: Labor intensity decreased by 25% due to an increase in labor productivity by 20%.
Problem 12: Calculations for Changing Productivity Growth and Labor Intensity Simultaneously
As a result of organizational measures, labor productivity in the team increased by 14.5%.
Partial modernization of equipment allowed reducing labor intensity by 7%.
Determine the growth for each measure separately.
Solution:
- Change in labor intensity due to the increase in labor productivity:
The change in labor intensity ΔI can be calculated using the formula:
ΔI= ΔPt / (100% - ΔPt ) * 100%
Where:
- ΔPt is the percentage increase in labor productivity.
ΔI = 14.5% / ( 100% - 14.5% ) * 100% ≈ 16.96%
The labor intensity of the product decreased by 16.96% due to an increase in labor productivity by 14.5%.
- Increase in labor productivity due to the decrease in labor intensity:
The increase in labor productivity ΔPt can be calculated using the formula:
ΔPt = ΔI / ( 100% - ΔI ) * 100%
Where:
- ΔI is the percentage decrease in labor intensity.
ΔPt = ( 7% / ( 100% - 7%) * 100% ≈ 7.53%
Labor productivity increased by 7.53% due to a decrease in labor intensity by 7%.
Answer: The first event led to a decrease in the labor intensity of the product by 16.96%,
and the second event led to an increase in labor productivity by 7.53%.
Problem 13: Determine the Decrease in Labor Intensity Due to an Increase in Labor Productivity
Labor productivity in the section increased by 16%, and the number of personnel remained unchanged.
Determine the decrease in labor intensity of products in the section and the change in production volume.
Solution:
- Change in production volume:
Since the number of workers remained unchanged, the production volume increased by 16%.
- Reduction in labor intensity:
The reduction in labor intensity ΔI can be calculated using the formula:
ΔI = ΔPt / ( 100% - ΔPt ) * 100%
Where:
- ΔPt is the percentage increase in labor productivity.
ΔI = 16% / ( 100% - 16% ) * 100% ≈ 19.05%
Labor intensity decreased by 19.05%.
Answer: The reduction in labor intensity was 19.05%, and the production volume increased by 16%.
Problem 14: Increase in Labor Productivity Due to Several Measures
The increase in labor productivity with the help of the first group of measures was 17%,
and with the help of the second by 7%. Determine the total change in labor productivity.
Solution:
Labor productivity changes due to the implementation of various measures at the enterprise. To find the total increase
in labor productivity due to several measures, you need to multiply the indices of growth (or decrease) in labor productivity.
- Find the total change in labor productivity:
ΔPt = 1.17 * 1.07 ≈ 1.2519
Labor productivity increased by 25.19% overall with the help of all the measures.
Answer: Labor productivity increased by 25.19% overall with the help of all the measures.
Labor productivity and headcount |
Описание курса
| Calculation of the number of workers
|

