|
|
Production Capacity
The Concept of Production Capacity
Production capacity is the maximum volume of products of appropriate quality and usual assortment that can be produced
by an enterprise in a certain period of time, provided that the equipment is operated efficiently and the labor resources are
used optimally.
Explanation of the Wording
-
Appropriate Quality: This implies that the products meet the standards adopted by the enterprise, the industry, and
the state for this type of product. The products do not have any additional defects and are produced using the
appropriate production technology.
-
Normal Assortment: This means that the production capacity indicator is calculated for the average set of types of
finished products typical for this enterprise. A nomenclature shift (a change in the product range or the proportions
between its types) leads to a different result than that obtained for the "normal assortment."
-
Time Period: This is the period during which production capacity is estimated. Depending on the purpose, the duration
of the production cycle, production features, etc., this can be an hour, a shift, a day, a decade, a month, a quarter,
a year, etc. The measurement period depends on the purpose for which the production capacity of the enterprise is
being assessed. For example, it is pointless to assess the production capacity of a shipbuilding plant in terms of an hour,
but for a mineral water bottling plant, such an indicator may be interesting.
Unit of Measurement of Production Capacity
The unit of measurement of production capacity is chosen based on the technological features of the enterprise.
For example:
-
For a cannery, it can be conventional cans.
-
For a brewery, it can be the number of dals of beer (1 dal is a decaliter).
-
For a machine-building enterprise that produces an assortment of certain types of equipment, it can be machine sets.
If the products are heterogeneous but there is a common technology, then sometimes the production capacity can be measured
in units of raw materials processed. Sometimes, in order to assess production capacity, both quantitative and qualitative
characteristics are needed. For example, in coal mining, we are interested in the production capabilities for extracting a certain
amount of coal from underground and the possibility of its delivery to the surface. To assess the "usefulness" of this activity,
the amount of extracted coal must be reduced to "marketable coal," that is, coal that must be enriched by removing impurities
from it. With a high ash content of mining, the amount of marketable products can differ significantly. Thus, for some industries,
two production capacity meters are used simultaneously - technological and marketable.
A very important factor that some authors often forget is the need to take into account limitations not only in terms of equipment
production capabilities but also in terms of labor resources. Some textbooks often ignore the fact that not only equipment but
also human labor can be a scarce resource. Therefore, to calculate production capacity, it is necessary to take into account both
factors.
Dynamics of Enterprise Production Capacity
Over time, the value of an enterprise's production capacity changes. This is due to various factors, the main of which are:
-
Natural Wear and Tear of Equipment: This entails a decrease in its productivity.
-
Planned Repairs: These cause equipment to stop for maintenance.
-
Introduction of New Units of Equipment: This can increase production capacity.
-
Introduction of New Capacities: This can also increase production capacity.
-
Equipment Modernization: This can change its productivity and quality characteristics.
-
Change in the Product Range or Proportions in the Existing Range: This is known as a structural shift.
-
Changes in the Composition of the Product, Raw Materials, Semi-Finished Products, Structures, etc.: These
changes can affect production capacity.
-
Changes in the Variability of the Enterprise's Work: This can impact production capacity.
-
Other Reasons: Various other factors can influence production capacity.
Thus, the calculated value of production capacity is not a constant value but is subject to periodic changes. Therefore,
when calculating, it is important to take into account the presence of an error in relation to the theoretical value.
Formula for Determining Production Capacity
In general, the production capacity of an enterprise (Pzag) can be determined by the following formula:
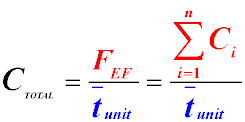
Where:
-
Fef – Effective fund of operating time of an enterprise (shop), equal to the sum of the capabilities (Ci)
of all production capacities.
-
tunit – Average labor intensity of manufacturing a unit of manufactured products.
Features of Determining Production Capacity
When determining the production capacity of an enterprise, the technological capabilities of shops, sections,
and individual units of equipment that impose restrictions on the production capabilities of this enterprise must
be taken into account. These are the so-called "bottlenecks."
Thus, the normal capacity of an enterprise is calculated taking into account bottlenecks and other restrictions.
These restrictions can vary, such as limitations on harmful emissions into the atmosphere.
Input and Output Capacity
According to the balance of production capacities, the following are determined and controlled by the management
of the enterprise:
-
Input Capacity (Ppoch): Determined at the beginning of the year from the available equipment.
-
Output Capacity (Pkin): Determined at the end of the planning period, taking into account the reduction and
addition of capacity due to capital construction, equipment modernization, technology improvement, and
production organization.
Formula for Calculating Production Capacity at the End of the Planning Period
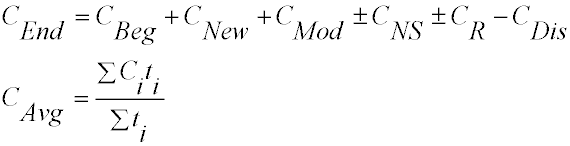
Where:
-
Cend – Capacity at the end of the period.
-
Cbeg – Capacity at the beginning of the period.
-
Cnew – Introduction of new capacities.
-
Cdis – Disposal of equipment.
-
ΔCns – Changes in production capacity as a result of a nomenclature shift.
-
ΔCr – Changes in production capacity as a result of equipment being put out for repair or returned from repair.
Average Production Capacity
Average production capacity is equal to the weighted average value of the measured production capacity. That is,
the sum of the products of production capacity for each period by the duration of such a period divided by the total
duration of all periods.
Maximum Production Capacity
There is also the concept of "maximum production capacity," when the enterprise operates in a mode that does not
correspond to the normal operating conditions of the equipment, such as increased working days ("rework") or the
introduction of additional working days. Such a mode of operation sometimes helps to fulfill the production program,
but it should be treated as if driving a car when the tachometer needle is in the "red zone." Such modes of operation
inevitably lead to increased wear and tear of equipment, an increase in the wage fund, and consequently, an increase
in the cost of a unit of production.
Efficiency of Production Capacity Utilization
The efficiency of the use of the enterprise's production capacity is determined using the production capacity utilization factor.
Types of Capacity
Three types of capacity are especially monitored:
-
Design Capacity: Provided for by the construction or reconstruction project.
-
Current Capacity: Actually achieved.
-
Reserve Capacity: To cover peak loads from 10% to 15%.
Average Annual Production Capacity
The average annual production capacity can also be determined by the following formula:
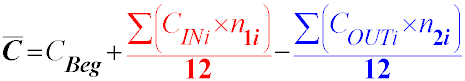
Where:
-
Cbeg – Production capacity at the beginning of the year.
-
Cin_i – Capacity put into operation.
-
Cout_i – Capacity taken out of operation.
-
n1_i – Number of months of operation of the i-th capacity put into operation during the year.
-
n2_i – Number of months after the i-th capacity is taken out of operation during the year.
Utilization Coefficient of Production Capacity
To characterize the use of potential production opportunities, the utilization coefficient of the average annual production
capacity is used:
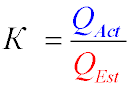
Where:
Production capacity and production efficiency |
Описание курса
| Calculation of production capacity
|

