Definition of a Cylinder and Its Elements
A cylinder (circular cylinder) is a three-dimensional geometric body consisting of two parallel circles that do not lie
in the same plane and are connected by a set of parallel line segments. These segments are called the generators
of the cylinder.
Elements of a Cylinder
- Bases: The two parallel circles are called the bases of the cylinder.
- Generators: The line segments connecting corresponding points on the circles' circumferences. These segments
form the lateral surface of the cylinder.
- Lateral Surface: The curved surface formed by the generators.
If the bases of the cylinder are not circles, the cylinder can be elliptical. However, such types of cylinders are usually not
considered in elementary geometry.
Alternative Definition
A cylinder can also be defined as a geometric body bounded by a cylindrical surface and two parallel planes intersecting it.
The full surface of a cylinder consists of the bases and the lateral surface.
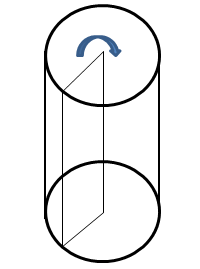
Types of Cylinders
- Straight Cylinder: A cylinder where the generators are perpendicular to the planes of the bases. A straight cylinder
can be visually represented as a body obtained by rotating a rectangle around one of its sides as an axis.
- Oblique Cylinder: A cylinder where the generators are not perpendicular to the planes of the bases.
Key Elements
- Radius: The radius of a cylinder is the radius of its base.
- Height: The height of a cylinder is the distance between the planes of its bases.
- Axis: The line passing through the centers of the bases. It is parallel to the generators.
Sections of a Cylinder
- Axial Section: A section of the cylinder with a plane passing through its axis. This section is a rectangle.
- Tangent Plane: A plane passing through a generator of the cylinder and perpendicular to the axial section plane
containing this generator.
Volume of a Cylinder
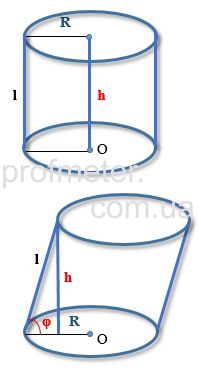
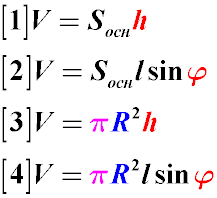
The volume of a cylinder is equal to the product of the area of the base and the height h [1]:
For a cylinder with a circular base, the volume is given by:
V=πR2×h [3]
where R is the radius of the base.
Lateral Surface Area of a Cylinder
The lateral surface area of a cylinder with radius RR of the base and height HH is given by:
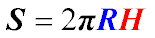
Total Surface Area of a Cylinder
The total surface area of a cylinder includes the areas of the two bases and the lateral surface:

Applications of Cylinders
Cylinders are commonly found in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and everyday objects. Examples include
pipes, tanks, and columns. Understanding the properties and calculations related to cylinders is essential for designing and
analyzing these structures.
Regular quadrangular prism |
Описание курса
| Cylinder with inscribed prism problems
|

