Problem 1: Find the Area Given Two Sides and the Angle Between Them
Problem: The sides of a triangle are 5 and 6 cm. The angle between them is 60 degrees. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
To solve this problem, we use the formula for the area of a triangle given two sides and the included angle:
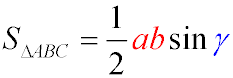
Given:
Substitute the values into the formula:
S = 1 / 2 × 5 × 6 × sin60°
Using the trigonometric value:
sin 60° = √3 / 2
So,
S = 1/2 × 5 × 6 × √3 / 2
S = 15 √3/2
Answer: 15√3 / 2
Problem 2: Find the Area of an Equilateral Triangle
Problem: Find the area of an equilateral triangle with a side of 3 cm.
Solution:
The area of an equilateral triangle can be found using the formula:
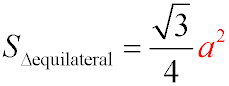
Given:
Substitute the value into the formula:
S=√3 / 4 × 32
S=√3 / 4 × 9
S=9 √3 / 4
Answer: 9√3 / 4 square cm.
Problem 3: Change in Area When Changing the Length of the Sides
Problem: How many times will the area of a triangle increase if the sides are increased by 4 times?
Solution:
Let's assume the original sides of the triangle are a, b, and c. The area of the original triangle can be found using Heron's formula:

If the sides are increased by 4 times, the new sides will be 4a, 4b, and 4c. The area of the new triangle will be:
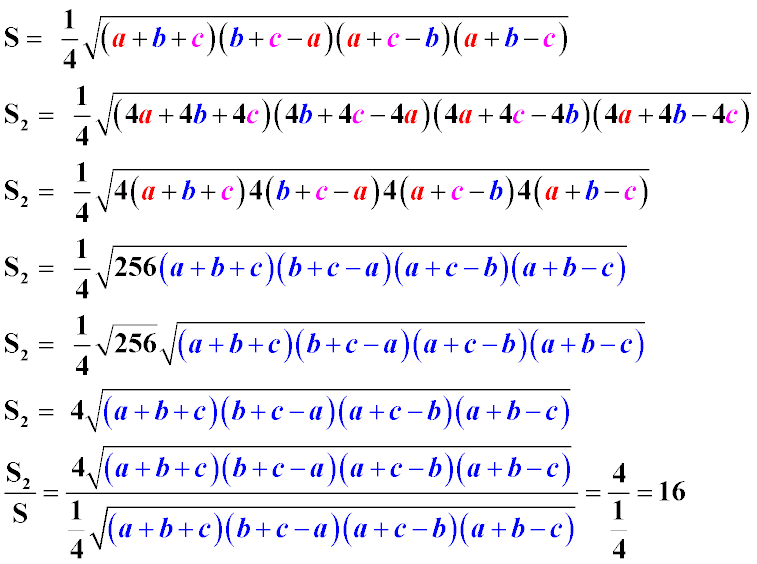
Answer: The area of the triangle will increase by 16 times.
Area of a triangle |
Описание курса
| Right Triangle
|

