General Principle of Transforming Functions of the Form α + a/bπ to a Simpler Form
To reduce the angle of a trigonometric function, the argument of the function must be presented in the form:
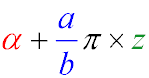
General Principle of Transforming Functions of the Form α + a/bπ to a Simpler Form
After this, you can use the rules and formulas listed below.
Rule 1: If a = 2, b = 1 and z is a natural number, the name of the function does not change
Formulas for Reducing the Argument of a Trigonometric Function for the Angle 2π for sin, cos, tg
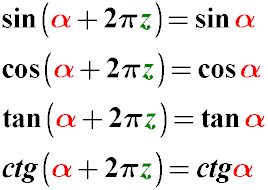
-
sin(α + 2π) = sin(α)
-
cos(α + 2π) = cos(α)
-
tan(α + 2π) = tan(α)
-
cot(α + 2π) = cot(α)
These equalities follow from the properties of the trigonometric circle.
Example: Simplify the expression cos(390).
Considering that π = 180 degrees, then: cos(390) = cos(30 + 2π) Using the reduction formula (2) above: cos(30 + 2π) = cos(30)
Rule 2: Subtracting the Angle α from 2π
Formulas for Reducing the Angle Argument of the Function sin, cos, tan 2π - α
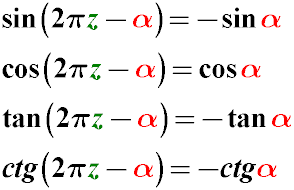
-
sin(2π - α) = -sin(α)
-
cos(2π - α) = cos(α)
-
tan(2π - α) = -tan(α)
-
cot(2π - α) = -cot(α)
These properties follow from the properties of the trigonometric circle, considering the parity of functions.
Example: Simplify the expression sin(345). Considering that π = 180 degrees, then: sin(345) = sin(2π - 15) Using the reduction formula (1) above:
sin(2π - 15) = -sin(15)
Rule 3: Adding the Angle π/2
If the argument of a trigonometric function contains the expression π/2 or n*π/2, where n is a natural odd number, the function changes according
to the following rules:
Formulas for Reducing the Argument of a Trigonometric Function of the Form α + π/2 for sin, cos, tan, cot
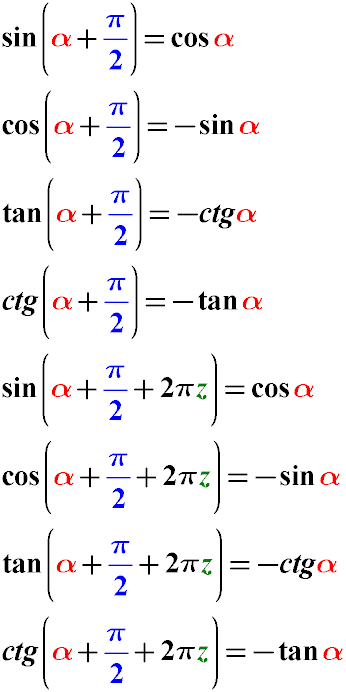
-
sin(α + π/2) = cos(α)
-
cos(α + π/2) = -cos(α)
-
tan(α + π/2) = -cot(α)
-
cot(α + π/2) = -tan(α)
From the properties of the trigonometric circle, it follows that:
-
sin(α + π/2 + 2π) = cos(α)
-
cos(α + π/2 + 2π) = -cos(α)
-
tan(α + π/2 + 2π) = -cot(α)
-
cot(α + π/2 + 2π) = -tan(α)
Example: Simplify the expression sin(α + 5π/2). sin(α + 5π/2) = sin(α + π/2 + 2π1) sin(α + π/2 + 2π1) = cos(α)
Rule 4: Subtracting the Angle π/2 (π/2 - α)
If the argument of a trigonometric function involves subtracting the angle π/2, for example, cos(π/2 - α), you can use the following transformation formulas:
Formulas for Reducing Trigonometric Functions When Subtracting the Angle π/2 - α for sin, cos, tg, cot
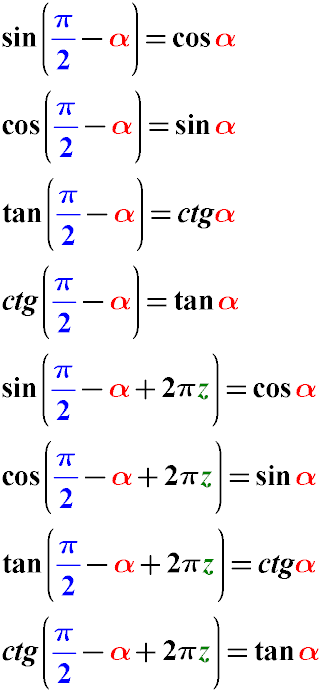
From the properties of a right triangle, it follows that:
-
sin(π/2 - α) = cos(α)
-
cos(π/2 - α) = sin(α)
-
tan(π/2 - α) = cot(α)
-
cot(π/2 - α) = tan(α)
From the properties of the trigonometric circle, it follows that:
-
sin(π/2 - α + 2π) = cos(α)
-
cos(π/2 - α + 2π) = sin(α)
-
tan(π/2 - α + 2π) = cot(α)
-
cot(π/2 - α + 2π) = tan(α)
Example: Simplify the expression cos(5π/2 - α). cos(5π/2 - α) = cos(π/2 - α + 2π1) cos(π/2 - α + 2π1) = sin(α)
Rule 5: Trigonometric Formulas for Reducing the Angle α + π
If the argument of a trigonometric function can be presented as the sum of angles of the form α + π + 2πz, such a function
can be reduced to a simpler form using the following formulas:
Trigonometric Formulas for Reducing the Angle α + π to a Simpler Form for sin, cos, tg, cot (α + π)
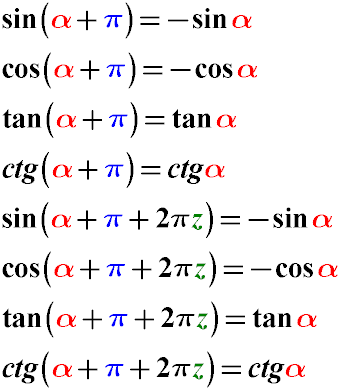
-
sin(α + π) = -sin(α)
-
cos(α + π) = -cos(α)
-
tan(α + π) = tan(α)
-
cot(α + π) = cot(α)
Also:
-
sin(α + π + 2π) = -sin(α)
-
cos(α + π + 2π) = -cos(α)
Example: Simplify the expression sin(7π + α). sin(7π + α) = sin(π + α + 2π3) sin(π + α + 2π3) = -sin(α)
Rule 6: Trigonometric Formulas for Reducing the Angle (π - α)
If the argument of a trigonometric function involves subtracting the angle π, i.e., simplifying the argument of the form (π - α), you can use the following formulas:
Formulas for Reducing the Argument of the Function π - α for sin, cos, tg, cot (π - α)
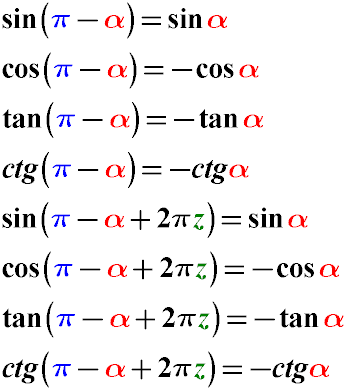
Example: Simplify the expression sin(5π - α). sin(5π - α) = sin(π - α + 2π2) sin(π - α + 2π2) = sin(α)
Rule 7: Trigonometric Formulas for Reducing Functions for Angles (3π/2 + α)
Formulas for Reducing Trigonometric Functions of the Form sin(α + 3π/2), cos(α + 3π/2), tg(α + 3π/2) to a Simpler Form
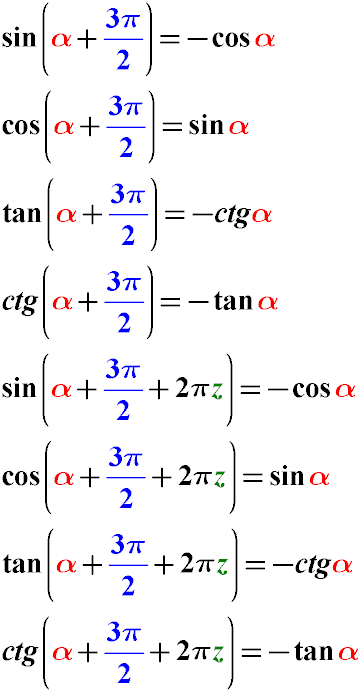
Example: Simplify the expression cos(α + 7π/2). cos(α + 7π/2) = cos(α + 3π/2 + 2π1) cos(α + 3π/2 + 2π1) = sin(α)
Rule 8: Trigonometric Formulas for Reducing the Argument for Cases of Subtracting the Angle α from 3π/2
Formulas for Reducing Trigonometric Functions with the Argument of the Angle of the Form (3π/2 - α) for sin(3π/2 - α),
cos(3π/2 - α), tg(3π/2 - α), cot(3π/2 - α)
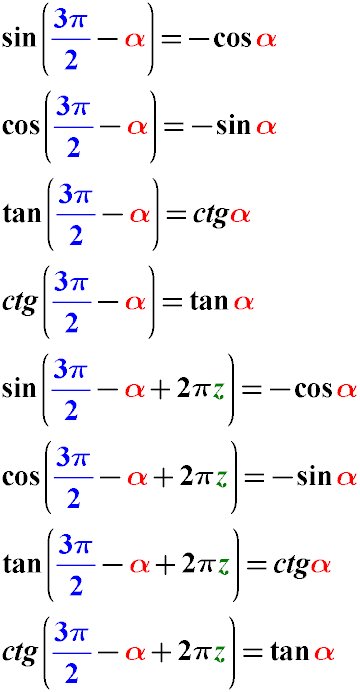
Example: Simplify the expression sin(7π/2 - α). sin(7π/2 - α) = sin(3π/2 - α + 2π1) sin(3π/2 - α + 2π1) = -cos(α)
Proof of the Correctness of the Formulas for Transforming Trigonometric Functions of the Form (α + a/bπ)
Values of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent of Acute Angles
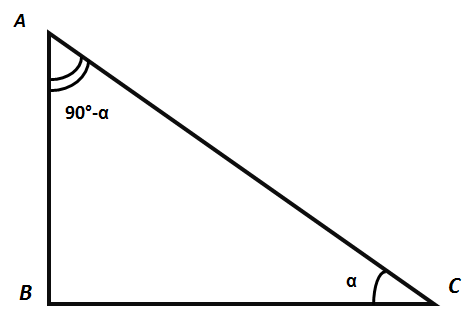
The values of trigonometric functions of acute angles are derived from the ratios of the sides of a right triangle.
THEOREM: For any acute angle α:
-
sin(90° - α) = cos(α)
-
cos(90° - α) = sin(α)
-
tg(90° - α) = ctg(α)
Consider a right triangle with an acute angle α. By the Pythagorean theorem:
AC² = AB² + BC².
Definition of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Angles 90 - α for a Right Triangle
By the definition of trigonometric functions:
Since ∠A + ∠C = 90°, then: ∠A = 90° - ∠C ∠A = 90° - α,
Comparing equalities (1) and (2), we write the identical equalities:
Calculate tg(90° - α), knowing that the tangent of an angle is the ratio of the sine and cosine of the same angle and using equality (3):
tg (90°-α) = sin(90°-α) / cos(90°-α) =cos α / sin α = ctg α.
Cosine of a double angle |
Описание курса
| Trigonometric formulas for lowering the degree sin cos tan
|

