|
|
Formulas for lowering the degree of trigonometric functions sin cos tan
When solving trigonometric equations, it is often necessary to lower the degree of the square, cube of the function sin cos tan. Sometimes it is necessary
to lower the degree of sine, cosine or tangent even of the fourth degree. In this case, you can use the following trigonometric identities that reduce the degree
of a trigonometric function to a regular sine, cosine, or tangent:
Formulas for reducing the degree of the trigonometric function sine:
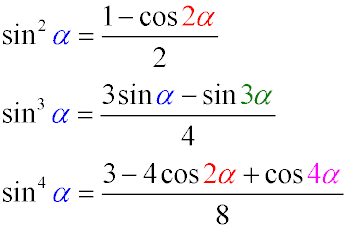
- The square of the sine of an angle is equal to half the difference between one and the cosine of twice the angle
- The sine cubed of an angle is equal to a quarter of the difference between three sines of this angle and the sine of three times the angle
- The sine to the fourth power of an angle is equal to one-eighth of the difference between three, four cosines of twice the angle
and the cosine of a quadrupled angle
Formulas for reducing the degree of the trigonometric function cosine:
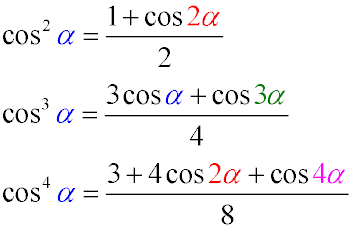
- The square of the cosine of an angle is equal to half the sum of one and the cosine of twice the angle
- The cosine cubed of an angle is equal to a quarter of the sum of three cosines of this angle and the cosine of three times the angle
- Cosine to the fourth power of an angle is equal to one eighth of the sum of three, four cosines of a double angle
and the cosine of a quadruple angle
Formulas for lowering the degree of the trigonometric function tangent:
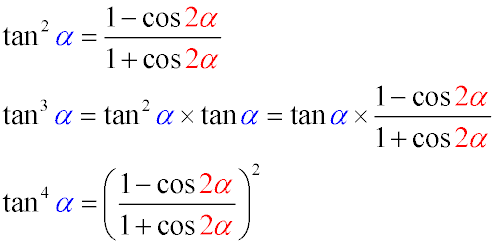
- The tangent squared of an angle is equal to the ratio of the square of the sine to the square of the cosine, which can also be expressed
as the ratio of the difference between unity and the cosine of a double angle to the sum of unity and the cosine of a double angle
- The tangent cubed of an angle is equal to the product of the tangent of the angle and the square of the tangent, which can also be expressed
as the product of the tangent of the angle and the ratio of the difference between unity and the cosine of a double angle to the sum of unity
and the cosine of a double angle
- The tangent to the fourth power of an angle is equal to the square of the ratio of the difference between unity and the cosine of a double angle
to the sum of unity and the cosine of a double angle
Formulas for lowering the degree of a trigonometric function cotangent:
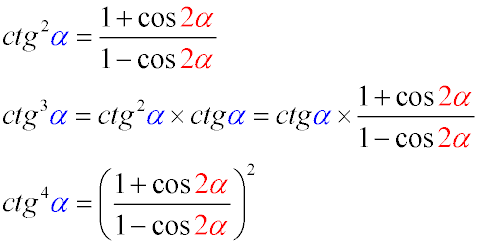
- cotangent squared of angle alpha is equal to the fraction whose numerator is one plus the cosine of twice the angle alpha,
and whose denominator is one minus the cosine of twice the angle alpha
-
cotangent cubed of angle alpha is equal to the product of cotangent squared of angle alpha and cotangent alpha, which is equal to
cotangent alpha multiplied by the fraction whose numerator is one plus the cosine of twice the angle alpha,
and whose denominator is one minus the cosine of twice the angle alpha
-
cotangent to the fourth power of angle alpha is equal to the fraction whose numerator is one plus the cosine of twice the angle alpha,
and whose denominator is one minus the cosine of twice the angle alpha, raised to the square
General Principle of Transforming Functions of the Form α + a/bπ to a Simpler Form |
Описание курса
| Trigonometric Circle
|

