Problem. The axial section of the cylinder is a square whose diagonal is 4 cm. Find the volume of the cylinder
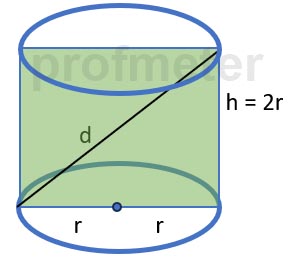
To solve this problem, let's break it down step by step:
- Find the side length of the square cross-section:
-
The diagonal of the square is given as 4 cm.
-
For a square, the relationship between the side length a and the diagonal d is given by the formula:
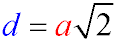
a = d / √2= 4 / √2 = 2√2 cm
-
Determine the radius of the cylinder:
-
The side length of the square is equal to the diameter of the cylinder's base.
-
Therefore, the radius rr of the cylinder is:
r = a / 2 = 2√2 / 2 = √2 cm
-
Find the height of the cylinder:
-
The height hh of the cylinder is equal to the side length of the square cross-section:
h = 2√2 cm
-
Calculate the volume of the cylinder:
-
The volume V of a cylinder is given by the formula:

V = π (√2)2(2√2) = π (2) (2√2) = 4√2π cm3
So, the volume of the cylinder is 4√2π cm3
Problem
Find the total surface area of a cylinder if the diagonal of its axial section, which is 8 cm, forms an angle of 30 degrees
with the generator of the cylinder.
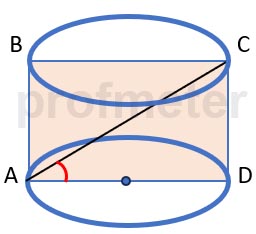
Solution
The cylinder has an axial section in the form of a parallelogram with the given diagonal angle.
Since AC = 8 cm and the angle ACD = 30°, then:
CD= AC⋅cos(30°)
Explanation: Triangle ACD is a right triangle. Therefore, CD/AC=cos(∠ACD) by the property of trigonometric functions in a right triangle.
The value of cos(30°) can be found from the table of trigonometric function values.
CD = 8⋅√3/2 = 4√3
Similarly,
AD=AC⋅sin(30°)
AD = 8⋅1/2 = 4
From this, the radius of the base of the cylinder is:
4 / 2 = 2 cm
The area of the base of the cylinder is:
S1 = πR2 = 4π
The lateral surface area of the cylinder is the area of its development - the product of the circumference of the base and the height of the cylinder.
That is:
S2 = 2πRh = 2π * 2 * 4√3 = 16π√3
The total surface area of the cylinder is:
S1+S2=4π+16π√3
Answer: 4π+16π√3
Cylinder and its sections (square and inscribed cube) |
Описание курса
|

