Angle Bisector
The word "bisector" is translated from French as "cutting in two". An angle bisector is a ray that divides an angle into two equal parts.
An angle bisector is a ray drawn from the vertex of an angle between its sides, dividing the angle in half.
Constructing an Angle Bisector Using a Protractor
An angle bisector can be constructed using the degree measure of an angle with a protractor. To do this, the degree measure of a given
angle is divided in half, and the degree measure of the half angle is laid off on one side from the vertex. The second side of such an angle
will be the bisector of the given angle.
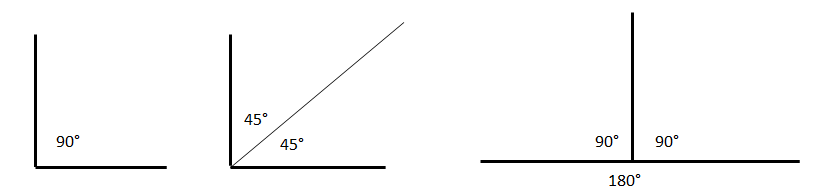
Bisector of a Right and Straight Angle
-
If a given angle has a degree measure of 60°, then two angles constructed using the bisector are 30° each, since 60°÷2=30°.
-
A straight angle is divided by a bisector into two right angles (180°÷2=90°).
-
Any obtuse angle is divided by a bisector into two acute angles.
Constructing an Angle Bisector Using a Compass and Ruler
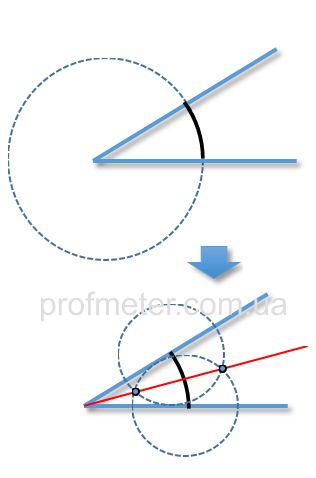
To construct an angle bisector without a protractor, using only a compass and ruler, follow these steps:
-
From the vertex of the angle, draw an arc of a circle with any radius so that it intersects the sides of the angle.
-
From each point of intersection of the arc and the sides of the angle, draw arcs of circles with the same radius.
-
Through the intersection points of the arcs, draw a ray from the vertex of the angle. This ray will be the bisector of the angle.
Bisector of the Angles of a Triangle
The bisector of an angle of a triangle is a segment of the bisector of the angle, drawn from the vertex of the angle to its intersection with the
opposite side.
A triangle has three bisectors, one drawn from each of its vertices.
The bisector of an angle of a triangle has many special properties, which are described in a separate article "Bisector of the Angles of a Triangle".
In any triangle ABC, in addition to the internal bisector, it is possible to draw external bisectors, which are bisectors of angles adjacent to
the internal angles of the triangle. In this case, the internal and external bisectors of the same angle are perpendicular. For more information, see
the article "Bisector of the External Angle of a Triangle".
Properties of Angle Bisectors
- Equidistant Property: Any point on the bisector of an angle is equidistant from the sides of the angle.
- Intersection Point: The bisectors of the angles of a triangle intersect at a single point called the incenter, which is the center of the inscribed
circle of the triangle.
- Perpendicularity: In a triangle, the internal and external bisectors of the same angle are perpendicular to each other.
Angle. Angles on the plane |
Описание курса
| Angle Bisector of a Triangle
|

